Cryopreserved Embryo Transfer (CEP)
Cryopreserved Embryo Transfer (CEP) is the process by which embryos cryopreserved during a previous IVF/ICSI cycle are thawed and transferred to the patient’s uterus.
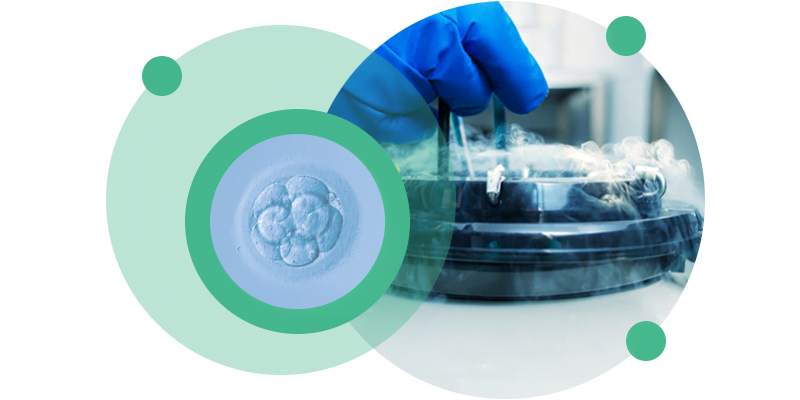
About cryopreserved of cryopreserved embryos
Cryopreserved embryo transfer is the process by which embryos cryopreserved during a previous IVF/ICSI cycle are thawed and transferred to the patient’s uterus. As well as thawing and transferring the embryos, this treatment involves preparing the endometrium to receive the embryos.
The endometrium is the layer of the uterus in which the embryos implant, and goes through several phases throughout a woman’s menstrual cycle. It is therefore essential that there is synchronisation between the embryo and the endometrium for implantation to take place.
An IVF/ICSI cycle often involves obtaining more good quality embryos than can be transferred to the patient’s uterus during that treatment cycle. These surplus embryos can be cryopreserved for use in a future cycle.
In other situations, it is not possible or advisable to transfer embryos into the IVF/ICSI treatment cycle in which they were created, either because of the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, or in cases where embryos have undergone pre-implantation genetic testing. Diagnosis and genetic results must be awaited.
There are also embryos that have been cryopreserved but whose recipients, after the necessary legal period has elapsed and with no intention of using them, donate them to other recipients (Embryo Donation).
In all these cases, a cycle of treatment is carried out to transfer cryopreserved embryos, which does not involve further ovarian stimulation, but does require preparation of the endometrium in order to increase its receptivity and increase the likelihood of embryo implantation and, consequently, pregnancy.
The CEP cycle involves preparing the endometrium to receive the embryos that will be transferred. Therefore, when you are ready to start CEP, whether after a previous unsuccessful treatment or for a new pregnancy, you should make an appointment with your doctor.
Medical appointment
An assessment is made of the best endometrial preparation protocol to follow. The number of embryos to be transferred is also discussed and informed consent for the transfer of cryopreserved embryos is signed by both members of the couple in the case of heterosexual couples or female couples.
Preparation of the endometrium
There are several endometrial preparation protocols, and it is possible to carry out the treatment in a natural cycle or in a medicated cycle.
- Natural cycle – a woman’s natural menstrual cycle is used, without the use of medication. Ultrasound scans are necessary to monitor changes in the thickness and ultrasound pattern of the endometrium, as well as changes in the ovarian follicle that develops during this cycle. You may be advised to undergo ovulation tests or receive medication to trigger ovulation. In this second part of the endometrial preparation, you may be advised to take oral and/or vaginal medication. The embryo transfer will take place approximately one week after ovulation.
- Hormone replacement cycle – in this case, drugs are used to replace the natural hormones. In the first part of endometrial preparation, oral oestrogens are used and monitoring ultrasounds are performed to assess the thickness and ultrasound pattern of the endometrium. Once optimal thickness has been achieved, progesterone is started vaginally and/or orally to complete endometrial preparation. Embryo transfer will take place approximately one week after the start of progesterone.
Thawing embryos
After scheduling the day of the ECT, the laboratory thaws the embryos so that they correspond in terms of day of development to the endometrial stage. At the CETI, with rare exceptions, embryos are cryopreserved at the blastocyst stage, which corresponds to the 5th or 6th day of embryonic development. In this case, the embryos are thawed a few hours before transfer. After thawing, the embryos are kept in culture in incubators with a suitable atmosphere and in culture media that promote embryonic development.
Embryo transfer
Embryo transfer is a rapid procedure without analgesia/sedation, in which one or more embryos are introduced into the uterine cavity using a catheter specifically designed for this purpose.
bHCG analysis
12 days after the embryo transfer, a blood sample is taken to detect the pregnancy hormone bHCG.
Embryo transfer is a non-invasive procedure, but afterwards it is advisable to rest for two days, abstain from sexual relations for 5 days and avoid strenuous physical effort until the pregnancy test has been carried out (12 days after the transfer).






Common questions
When preparing the endometrium for an ECT cycle, you may need to undergo an average of two to three surveillance ultrasounds.
The national and international success rate for ECT is over 40%. Since the success of any assisted reproduction treatment depends on many factors, you should discuss your particular case with your doctor.
Under current Portuguese law, embryos can remain in cryopreservation for a period of 3 years, renewable for a further 3 years.
If you do not wish to transfer your cryopreserved embryos, you may consent to their donation to other recipients of Medically Assisted Reproduction treatments or to their donation to scientific research projects. If you do not consent to either of these, the embryos will be thawed and discarded.
Although embryo vitrification is a technique that has been tried and tested in assisted reproduction laboratories, it is not possible to guarantee that the embryo will withstand the freezing and thawing procedures. However, the embryo survival rate is quite high and situations in which an embryo does not survive the procedure are rare. It is important that these techniques are carried out by experienced professionals.
You can consult the CETI price list here.
